Genuine commitment to your health.

ABOUT US
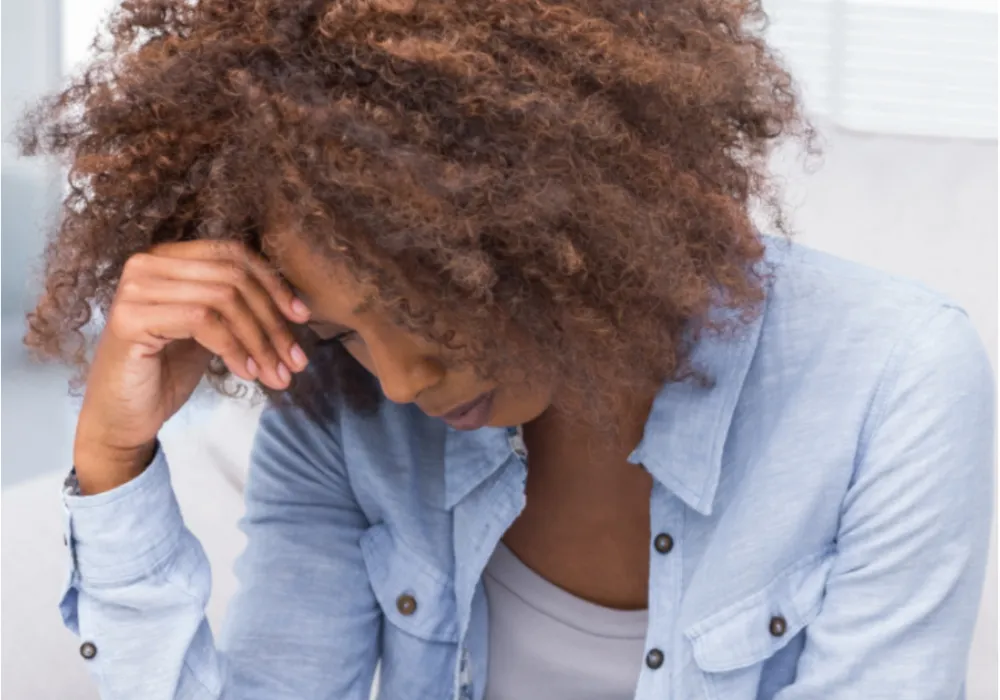
Who We Are
We are comprehensive health care clinic that focuses on mental and physical rehabilitation. Our primary goal is to help clients return to daily life with strength and confidence to handle life demands. Our comprehensive approach looks at the whole person and factors all aspect of life that affects our client’s participation in occupations. Our specially trained staff is committed to providing successful treatments that are client-centered and build rapport. Services we offer to ensure success with our clients include:

Our Mission Statement
Our mission is to provide rehabilitative services to clients that experience depression, pain, and/or decline in functional performance that affects their daily occupations. Stone Star is dedicated to restoring function, strength, and hope to our clients to help them live a better life.

OUR DEDICATION
Why Stone Star
We offer research proven effective treatment for depression, pain, and functional decline. Our TMS therapy
is the number one recommended treatment for major depressive disorder. We specialize in a comprehensive treatment approach that offers non- drug, non-Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), and non-surgical methods. In addition, our specially trained staff is committed to providing successful treatments that are client-centered and build rapport. Lastly, our facility is a haven for clients to feel comfortable and cared for with the top-notch services and equipment.
READY TO GET YOUR DOT physical exam
Stay compliant and get back on the road with our Dot Physical Exams. Our certified professionals ensure you meet Department of Transportation (DOT) with thorough and efficient exams.







Facebook
Instagram
X
LinkedIn
Youtube
TikTok